When it comes to TMJ surgery, there’s a bit of a gray area between medical and dental. You see, the temporomandibular joint is the joint that connects your jawbone to your skull, allowing you to open and close your mouth, chew, and speak. When this joint becomes misaligned or damaged, it can cause a range of symptoms like jaw pain, headaches, and difficulty in opening and closing the mouth. Now, here’s where things get interesting – the treatment for TMJ disorders can involve both medical and dental approaches.

Is TMJ Surgery Medical or Dental?
TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders can cause significant pain and discomfort in the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered as an option. However, there is often confusion about whether TMJ surgery falls under the domain of medical or dental professionals. In this article, we will explore the nature of TMJ surgery and the professionals involved in its management.
What is TMJ Surgery?
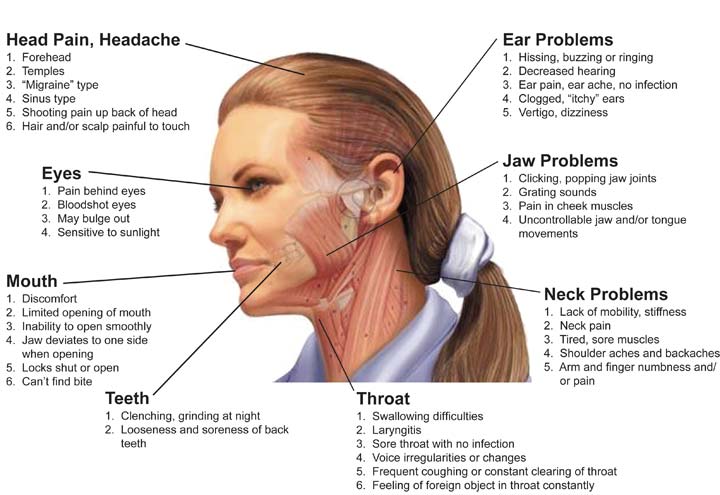
TMJ surgery refers to the various surgical procedures performed to address disorders of the temporomandibular joint. The temporomandibular joint is the joint that connects the jawbone to the skull, allowing for movements such as chewing and speaking. TMJ disorders can result in symptoms like jaw pain, clicking or popping sounds, limited jaw movement, and headaches.
The decision to undergo TMJ surgery is typically made when conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and splints have failed to alleviate symptoms. Surgery aims to correct structural abnormalities, reduce inflammation, and restore normal function to the jaw joint. There are different types of TMJ surgery, including arthroscopy, open-joint surgery, and joint replacement.
The Role of Medical Professionals in TMJ Surgery
TMJ surgery involves the expertise of both medical and dental professionals.
Medical professionals, such as oral and maxillofacial surgeons, play a crucial role in performing the surgical procedures. These surgeons have specialized training in the surgical management of conditions affecting the mouth, jaw, and face.
During TMJ surgery, medical professionals may perform arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a small camera into the joint to visualize and treat any abnormalities. They may also perform open-joint surgery, which involves making a larger incision to access the joint directly. In some cases, joint replacement may be necessary, where the damaged joint is replaced with an artificial joint.
The Role of Dental Professionals in TMJ Surgery
While medical professionals perform the surgical aspect of TMJ surgery, dental professionals play a crucial role in the diagnosis, pre-surgical planning and last and most important, maintaining your bite and jaw alignment.
Dentists, particularly those with expertise in orofacial pain and temporomandibular disorders, are responsible for evaluating the condition and determining if surgery is necessary.
Dental professionals may also provide non-surgical treatments such as occlusal splints, which are custom-made oral appliances that help align the jaw, maintain your bite and alleviate symptoms. They may work closely with medical professionals to ensure a comprehensive approach to the management of TMJ disorders.
In conclusion, TMJ surgery is a multidisciplinary field that involves the collaboration of both medical and dental professionals. Medical professionals, such as oral and maxillofacial surgeons, perform the surgical procedures to address TMJ disorders. Dental professionals, on the other hand, play a crucial role in diagnosis, pre-surgical planning, and providing non-surgical treatments. The combined expertise of both medical and dental professionals ensures comprehensive care for individuals with TMJ disorders.
Key Takeaways: Is TMJ Surgery Medical or Dental?
- TMJ surgery falls under both medical and dental fields.
- TMJ stands for temporomandibular joint, which connects the jaw to the skull.
- Medical professionals, such as oral and maxillofacial surgeons, perform TMJ surgeries.
- Dental professionals, including orthodontists and prosthodontists, also play a role in diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders.
- TMJ surgery aims to correct structural or functional issues with the jaw joint and surrounding muscles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TMJ surgery and who performs it?
TMJ surgery, also known as temporomandibular joint surgery, is a procedure performed to treat disorders or conditions affecting the temporomandibular joint. This joint connects the jawbone to the skull and is responsible for the movement of the jaw. TMJ surgery is a specialized procedure that can be performed by both medical and dental professionals, depending on the specific case.
In some instances, TMJ surgery may be performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons, who are dental specialists with advanced training in surgical procedures involving the face, mouth, and jaw. They are experienced in diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders and can provide surgical interventions when necessary. On the other hand, in more complex cases or when there are underlying medical conditions involved, TMJ surgery may be performed by maxillofacial or craniofacial surgeons who are medical professionals specializing in surgical procedures involving the head, face, and jaw.
What are the common reasons for TMJ surgery?
TMJ surgery is typically recommended when conservative treatments have failed to alleviate symptoms or when the condition is severe and significantly affects the patient’s quality of life. Some common reasons for TMJ surgery include:
1. Severe pain: If a patient experiences chronic, debilitating pain in the jaw joint or surrounding areas that is not relieved by non-surgical treatments, surgery may be considered.
2. Joint damage: In cases where there is significant damage to the temporomandibular joint, such as arthritis, degenerative joint disease, or structural abnormalities, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the joint.
3. Jaw misalignment: If the jaw is misaligned or there are issues with the bite that cannot be corrected with orthodontic treatment alone, TMJ surgery may be recommended to reposition the jaw and improve overall function.
4. Lockjaw or limited jaw movement: When the jaw becomes locked or there is restricted movement due to a TMJ disorder, surgery may be performed to release the joint and restore normal jaw function.
5. Resistant to other treatments: If other conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, or splint therapy have been ineffective in managing TMJ symptoms, surgery may be considered as a last resort.
It is important to note that the decision to undergo TMJ surgery should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional who can evaluate the individual case and determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
What are the different types of TMJ surgery?
There are several different types of TMJ surgery, and the specific procedure recommended will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the TMJ disorder. Some common types of TMJ surgery include:
1. Arthroscopy: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera and surgical instruments into the joint through small incisions. It allows the surgeon to visualize and treat the joint without the need for open surgery.
2. Joint replacement: In cases where the joint is severely damaged or has degenerated, joint replacement may be necessary. This involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial joint made of metal or plastic.
3. Joint repair: If there are structural abnormalities or specific issues with the joint, surgery may be performed to repair or reconstruct the joint. This can involve removing scar tissue, repositioning the disc, or reshaping the joint surfaces.
4. Orthognathic surgery: Also known as corrective jaw surgery, this procedure is performed to correct severe jaw misalignment or abnormalities that contribute to TMJ disorders. It involves repositioning the jaws to improve overall function and alignment.
5. Nerve decompression: In rare cases where a nerve is compressed or entrapped, surgery may be performed to release the nerve and alleviate symptoms.
It is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine which type of TMJ surgery is most suitable for your specific condition.
What is the recovery process like after TMJ surgery?
The recovery process after TMJ surgery can vary depending on the specific procedure performed and the individual’s healing ability. Generally, patients can expect some swelling, discomfort, and limited jaw movement in the immediate post-operative period. Pain medication and ice packs may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce swelling.
In the days following surgery, a soft or liquid diet may be recommended to avoid putting excessive pressure on the jaw joint. Physical therapy exercises and jaw stretching exercises may also be prescribed to improve mobility and prevent stiffness.
The length of the recovery period can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the extent of the surgery and individual healing. It is important to follow all post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon, attend follow-up appointments, and report any concerning symptoms or complications.
Are there any risks or complications associated with TMJ surgery?
Like any surgical procedure, TMJ surgery carries potential risks and complications. These can vary depending on the specific procedure performed and individual factors. Some potential risks and complications may include:
1. Infection: There is a risk of infection at the surgical site, which may require antibiotics and additional treatment.
2. Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery may occur, requiring medical intervention.
3. Nerve injury: There is a small risk of nerve damage during surgery, which may result in temporary or permanent numbness, tingling, or weakness in the face or jaw.
4. Joint stiffness: Some patients may experience temporary or permanent jaw stiffness or limited range of motion after surgery.
5. Anesthesia complications: General anesthesia carries its own risks, including allergic reactions, respiratory problems, or adverse reactions to medications.
It is essential to discuss the potential risks and complications with the surgeon before undergoing TMJ surgery and to follow all pre- and post-operative instructions to minimize these risks. Regular communication with the healthcare team is crucial to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
Is TMJ a medical or dental problem?
Final Summary: Is TMJ Surgery Medical or Dental?
After exploring the intricacies of TMJ (temporomandibular joint) surgery, it is clear that this procedure falls under both the medical and dental realms. While some aspects of TMJ surgery are handled by medical professionals, such as oral and maxillofacial surgeons, other aspects require the expertise of dental specialists. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive care and the best possible outcomes.
In conclusion, TMJ surgery is a collaboration between medical and dental professionals, combining their knowledge and skills to address the complexities of this condition. Whether it’s the medical side focusing on diagnosing the underlying causes or the dental side providing treatments like orthodontics or oral appliances, both disciplines play a crucial role in managing TMJ disorders. By acknowledging the importance of this interdisciplinary approach, patients can access the most effective and personalized care for their TMJ concerns.
Call or Book appointment online
:Ace Dental Care Alpharetta office: 678-562-1555 - Book Now
Ace Dental Care Norcross office: 770-806-1255 - Book Now
Disclaimer
This blog post was generated by artificial intelligence. The content of this post may not be accurate or complete, and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional advice. If you have any questions about the content of this post, please contact us.
We are constantly working to improve the accuracy and quality of our AI-generated content. However, there may still be errors or inaccuracies. We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.





