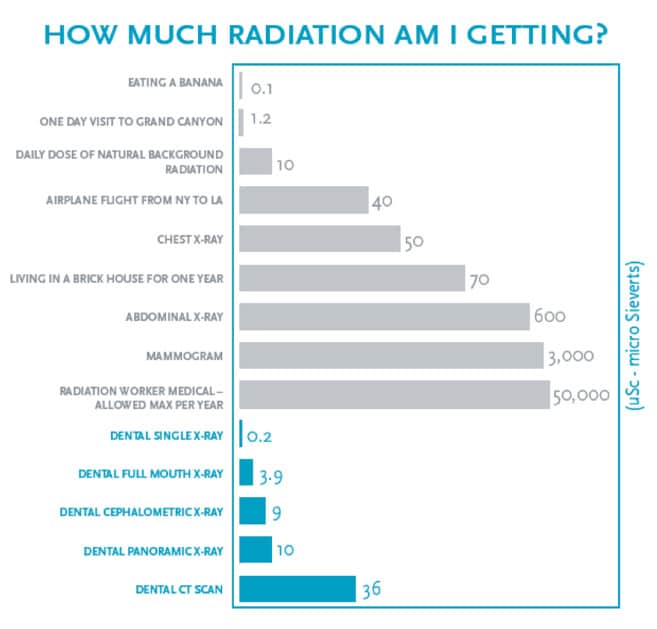
Dental X-rays are a common dental diagnostic tool that raises concerns about radiation exposure. However, dental X-ray radiation is relatively low, similar to the exposure during a short flight or a day in the sun. Dentists take precautions to minimize exposure, like lead aprons and high-speed film, ensuring the safety of these essential tools for maintaining oral health.
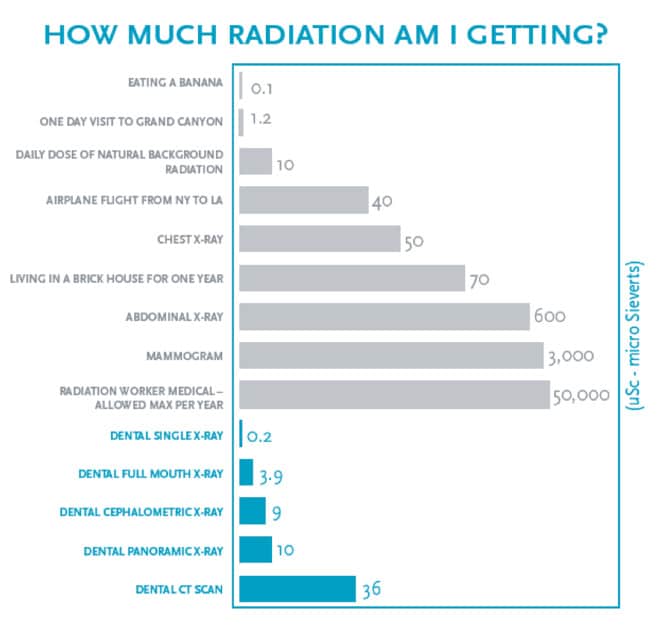
Understanding Dental X-ray Radiation Exposure
Radiation exposure is a concern for many individuals, especially when it comes to medical procedures. Dental X-ray radiation, in particular, has raised questions about the amount of exposure to patients and dentists during these routine examinations. It’s essential to understand the potential risks and benefits associated with dental x-rays and how they contribute to overall radiation exposure. By examining the facts and taking necessary precautions, patients can make informed decisions about their oral health.
- Definition of Dental X-rays: Dental x-rays, also known as dental radiographs, are diagnostic tools employed by dentists to evaluate oral health. They capture detailed images of the mouth to identify dental conditions like cavities, gum disease, and impacted teeth.
- Radiation Usage: During a dental x-ray, a small amount of radiation is employed to produce an image. An x-ray machine emits radiation that passes through the mouth and interacts differently with oral structures. This differential interaction creates a shadow-like image on x-ray film or a sensor.
- Purpose of Dental X-rays: These images help dentists to:
- Detect cavities: X-rays reveal cavities between teeth that might be missed during a visual examination.
- Assess gum health: They show bone loss due to gum disease.
- Locate impacted teeth: X-rays pinpoint teeth that haven’t erupted properly.
- Plan treatments: Dentists use x-rays to plan procedures like root canals or extractions.
- Monitor overall oral health: Regular x-rays track changes over time.
Types of Dental X-rays
There are several types of dental x-rays commonly used in dental practices. These include:
1. Bitewing X-rays: These x-rays focus on the upper and lower back teeth. They help dentists detect decay between teeth, assess the fit of dental restorations, and evaluate bone density.
2. Periapical X-rays: Periapical x-rays capture the entire tooth, from the crown to the root. They are used to identify issues such as abscesses, impacted teeth, and root infections.
3. Panoramic X-rays: Panoramic x-rays provide a broad view of the entire mouth, including the teeth, jaws, sinuses, and nasal area. They are useful for evaluating overall oral health, identifying abnormalities, and planning orthodontic or surgical treatments.
4. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): CBCT scans offer a three-dimensional view of the oral structures, providing detailed information for complex dental procedures, such as dental implant placement and orthodontic treatment planning.
The Importance of Dental X-rays
Diagnostic Role: Dental x-rays are crucial for diagnosing and treating oral health conditions. They reveal hidden problems like cavities between teeth, impacted wisdom teeth, or jawbone abnormalities not visible to the naked eye, enabling early and less invasive treatment.
Monitoring Progression: X-rays aid in monitoring dental diseases and treatment effectiveness. They provide a baseline for comparisons, helping dentists make informed decisions about treatment plans, ensuring better patient care.
The Amount of Radiation Exposure: Concerns about radiation exposure exist, but dental x-rays emit minimal radiation. Advanced technology has significantly reduced doses, making them safe for routine use.
About Radiation Doses: Radiation exposure is measured in millisieverts (mSv). Dental x-rays have low doses, ranging from 0.005 to 0.01 mSv, much lower than natural background radiation.
Benefits Outweigh Risks: Benefits of early disease detection far outweigh minimal radiation risks. Dentists follow strict protocols, using lead aprons and thyroid collars for patient protection.
Minimizing Exposure: Dentists adhere to the ALARA principle to minimize radiation exposure, ensuring that they use the lowest dose needed for diagnosis.
Frequency of Dental X-rays: The frequency of dental x-rays varies based on age, oral hygiene, medical history, and existing dental issues. Bitewing x-rays are typically taken every 6 to 18 months.
Pregnancy and Dental X-rays: Dental x-rays are generally safe during pregnancy with proper shielding. Dentists may postpone non-urgent x-rays or use additional shielding methods.
Alternative Diagnostic Tools: Dentists may use alternative diagnostic tools, like intraoral cameras or digital scanners, when appropriate, but these may not offer the same information as x-rays.
The Importance of Informed Decision-Making: Patients should be well-informed and involved in decision-making. Dentists should explain benefits, risks, and precautions, fostering trust and patient-centered care.
Dental x-rays are vital for diagnosis and treatment, offering benefits that surpass minimal radiation risks. Dentists ensure safety, and patient involvement is key to balanced oral health care.
Key Takeaways: How Much Radiation Exposure from Dental X-rays?
- Dental X-rays expose you to a small amount of radiation.
- The radiation levels from dental X-rays are considered safe for most people.
- Modern dental X-ray machines use low radiation doses to minimize exposure.
- Lead aprons and thyroid collars are used to protect sensitive areas during X-rays.
- Regular dental X-rays are important for detecting oral health issues early on.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are dental x-rays safe?
Dental x-rays are safe due to minimal radiation, modern technology, and careful dose management by dentists. The benefits of diagnosis outweigh radiation risks. Pregnant women should inform their dentists to avoid unnecessary x-rays and protect the fetus from radiation.
How much radiation do dental x-rays emit?
Dental x-rays emit minimal radiation, typically 0.005 to 0.01 µSv, akin to 1-2 days of natural background radiation exposure. Digital x-ray systems may emit even lower doses. Importantly, dental x-ray radiation is much lower than in procedures like CT scans or chest x-rays.
Do children receive more radiation from dental x-rays?
Children may receive slightly higher radiation doses from dental x-rays due to their smaller and more radiation-sensitive bodies. Dentists use pediatric-sized equipment and adjust settings to minimize exposure. Recommendations from dental organizations, like the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, include using lead aprons and thyroid collars to further reduce radiation exposure in children during x-rays.
How often should dental x-rays be taken?
The frequency of dental x-rays varies based on factors like oral health, history, and risks. Typically, adults get bitewing x-rays every 1-2 years and full-mouth series x-rays every 3-5 years. Children, at higher risk, might need more frequent x-rays. Dentists assess individual needs for optimal oral health.
What precautions are taken to minimize radiation exposure during dental x-rays?
Dentists minimize radiation exposure during x-rays through precautions like lead aprons, thyroid collars, and modern digital systems emitting lower radiation doses. They adhere to the ALARA principle, keeping radiation doses as low as necessary for accurate diagnosis, using proper techniques and positioning, and taking x-rays only when clinically required.
Are Dental X-rays Safe?
Final Thoughts
Radiation exposure from dental X-rays strikes a balance between benefits and potential risks. While they entail minimal radiation, modern dentistry adheres to stringent safety measures, employing lead aprons, thyroid collars, and advanced techniques to limit exposure. X-ray frequency is tailored to individual needs, reducing unnecessary radiation.
Dental X-rays are crucial for diagnosing oral health issues, with benefits far outweighing minimal radiation risks. Dental professionals prioritize safety while delivering effective care. Rest assured, during your next dental visit, the radiation exposure from X-rays remains well within safe limits.
Call or Book appointment online
:Ace Dental Care Alpharetta office: 678-562-1555 - Book Now
Ace Dental Care Norcross office: 770-806-1255 - Book Now
Disclaimer
This blog post was generated by artificial intelligence. The content of this post may not be accurate or complete, and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional advice. If you have any questions about the content of this post, please contact us.
We are constantly working to improve the accuracy and quality of our AI-generated content. However, there may still be errors or inaccuracies. We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.





