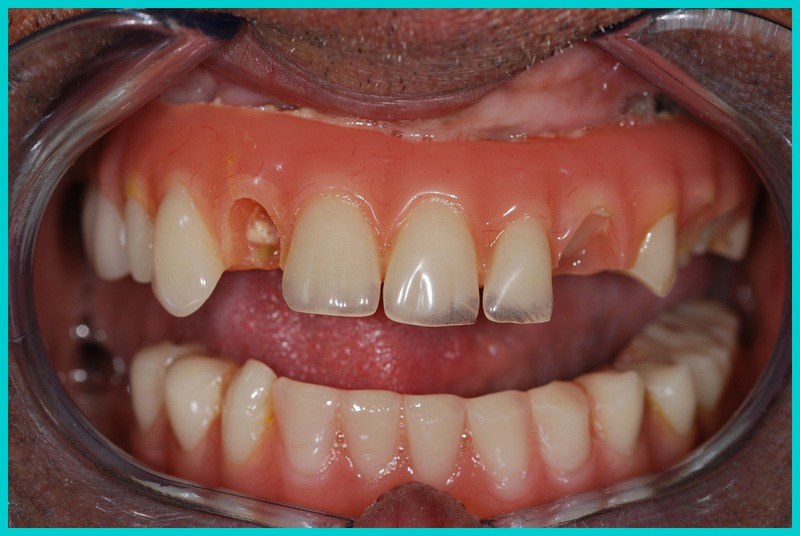
Dental implants offer a reliable solution for smile restoration, but concerns about their longevity may arise. Complications like infection, implant failure, or peri-implantitis can occur, though they’re rare. Understanding potential issues, prevention methods, and appropriate actions in case of problems ensures the durability of dental implants.
Can Dental Implants Go Bad?
Can Dental Implants Go Bad?
Dental implants are a popular and effective solution for replacing missing teeth. They are designed to be a long-term solution, providing stability, functionality, and aesthetics. However, like any medical procedure, there are risks and potential complications associated with dental implants. In this article, we will explore the question, “Can dental implants go bad?” and discuss the factors that can contribute to implant failure.
Understanding Dental Implants
Dental implants are titanium posts that are surgically inserted into the jawbone to replace missing teeth. These implants act as artificial tooth roots, providing a strong foundation for dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. The implant fuses with the surrounding bone through a process called osseointegration, creating a stable and durable base for the replacement tooth.
In most cases, dental implants have a high success rate and can last for many years or even a lifetime with proper care. However, there are situations where implants can encounter problems and potentially fail.
Factors That Can Contribute to Implant Failure
While dental implant failure is relatively rare, there are several factors that can increase the risk:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for the long-term success of dental implants. Neglecting oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, can lead to the accumulation of plaque and bacteria around the implant site, increasing the risk of infection and implant failure.
2. Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for dental implant failure. It impairs the body’s ability to heal and can decrease the success rate of implant osseointegration. If you are a smoker, it is advisable to quit or at least reduce your smoking habits before undergoing dental implant surgery.
3. Gum Disease: Pre-existing gum disease can compromise the success of dental implants. Periodontal infections can weaken the supporting structures around the implant, leading to bone loss and implant failure. It is essential to have a healthy periodontal condition before considering dental implant treatment.
4. Insufficient Bone Density: Adequate bone density is necessary for successful implant placement. If the jawbone lacks the required density or volume, additional procedures such as bone grafting may be needed to ensure a secure implant anchorage. Insufficient bone density can increase the risk of implant failure.
5. Medical Conditions and Medications: Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and uncontrolled gum disease can affect the healing process and increase the risk of implant failure. Additionally, medications like bisphosphonates, which are commonly used to treat osteoporosis, can interfere with implant osseointegration.
It is important to note that while these factors can increase the risk of implant failure, they do not necessarily mean that dental implants will go bad in every case. With proper evaluation, treatment planning, and diligent oral care, the chances of implant failure can be significantly minimized.
Signs of Implant Failure
In some cases, dental implants may exhibit signs of failure or complications. It is important to be aware of these signs and seek immediate dental attention if you experience any of the following:
1. Persistent Pain or Discomfort: While some discomfort is expected during the initial healing period, persistent pain or discomfort around the implant site can be a sign of implant failure or infection.
2. Swelling and Redness: Swelling and redness around the implant site can indicate an inflammatory response or infection. It is important to monitor the gum tissue around the implant and report any changes to your dentist.
3. Mobility or Shifting of the Implant: A stable dental implant should not move or shift. If you notice any mobility or changes in the position of the implant, it may indicate a problem with the implant’s integration or stability.
4. Gum Recession: Receding gum tissue around the implant can expose the implant surface, making it more susceptible to infection and failure. Regular check-ups with your dentist can help identify early signs of gum recession.
If you experience any of these signs, it is important to consult with your dentist as soon as possible. Early intervention can help address the issue before it progresses further.
Preventing Implant Failure
While dental implant failure is not always preventable, there are steps you can take to minimize the risk and increase the longevity of your implants:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help prevent plaque buildup and reduce the risk of infection.
2. Quit Smoking: If you are a smoker, quitting or reducing your smoking habits can significantly improve the success rate of dental implant treatment.
3. Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular dental visits allow your dentist to monitor the health of your implants and address any potential issues early on.
4. Follow Post-Operative Instructions: After implant surgery, it is crucial to follow your dentist’s post-operative instructions, including proper oral hygiene practices and any prescribed medications.
5. Address Underlying Health Conditions: If you have medical conditions that can affect implant success, work closely with your healthcare team to manage and control these conditions.
In conclusion, while dental implants can go bad in certain circumstances, proper evaluation, treatment planning, and diligent oral care can significantly reduce the risk of implant failure. Regular dental check-ups and early intervention are essential to ensure the long-term success and functionality of dental implants.
Remember, each individual case is unique, and it is important to consult with your dentist to determine the best course of action for your specific situation. With proper care and maintenance, dental implants can provide a stable and aesthetically pleasing solution for missing teeth.
Key Takeaways: Can Dental Implants Go Bad?
- Dental implants can sometimes fail due to various reasons.
- Common reasons for dental implant failure include infection, bone loss, and poor oral hygiene.
- Regular dental check-ups and proper oral care can help prevent dental implant complications.
- Smoking and certain medical conditions can increase the risk of implant failure.
- If a dental implant does fail, it can be replaced or repaired by a dental professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to dental implants, it’s natural to have questions and concerns. One common query is whether dental implants can go bad. In this section, we address this important question and provide detailed answers to help you understand the potential risks and outcomes associated with dental implants.
1. How long do dental implants last?
Dental implants are designed to be a long-term solution for missing teeth. With proper care and maintenance, they can last a lifetime. However, it’s important to note that individual experiences may vary. Factors such as oral hygiene practices, overall health, and lifestyle habits can influence the longevity of dental implants.
Regular dental check-ups and diligent oral hygiene routines, including brushing, flossing, and rinsing with mouthwash, can significantly contribute to the long-term success of dental implants. Additionally, avoiding habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also help prevent complications that may impact the lifespan of dental implants.
2. Can dental implants become infected?
While dental implants are generally considered safe and successful, they can become infected in rare cases. Peri-implantitis is a condition characterized by inflammation and infection around the dental implant. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk of developing peri-implantitis.
To reduce the risk of infection, it is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene practices and attend regular dental check-ups. Your dentist may also recommend special cleaning techniques or prescribe antibiotics if you are at a higher risk of infection. Early detection and prompt treatment of peri-implantitis can help prevent further complications and preserve the integrity of the dental implant.
3. What are the signs of a failing dental implant?
A failing dental implant may exhibit various signs and symptoms. These can include pain or discomfort around the implant site, swelling, redness, or bleeding of the gums, loosening of the implant, or a change in the bite. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult your dentist as soon as possible.
Your dentist will conduct a thorough examination and perform diagnostic tests to determine the cause of the implant’s failure. In some cases, the implant may need to be removed and replaced. Early intervention can improve the chances of successful implant revision and prevent further complications.
4. Can dental implants fail due to bone loss?
Bone loss can potentially impact the stability and longevity of dental implants. In some cases, inadequate bone density or poor bone quality may prevent successful implant integration. Additionally, excessive bone loss around an already placed implant can lead to its failure.
To minimize the risk of implant failure due to bone loss, your dentist will assess the quality and quantity of your jawbone before the implant procedure. If bone loss is a concern, your dentist may recommend bone grafting or other procedures to enhance the bone structure and ensure a secure foundation for the implant.
5. Can dental implants be replaced if they go bad?
If a dental implant fails or develops complications, it may be necessary to replace it. The process of replacing a failed implant involves removing the implant and addressing any underlying issues that contributed to its failure. Once the area is healed and ready, a new implant can be placed.
Your dentist will evaluate the specific circumstances surrounding the implant failure and develop a personalized treatment plan for replacement. By addressing the underlying causes and ensuring proper healing, the success rate of the replacement implant can be maximized.
Conclusion: The Verdict on Dental Implants
Call or Book appointment online
:Ace Dental Care Alpharetta office: 678-562-1555 - Book Now
Ace Dental Care Norcross office: 770-806-1255 - Book Now
Disclaimer
This blog post was generated by artificial intelligence. The content of this post may not be accurate or complete, and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional advice. If you have any questions about the content of this post, please contact us.
We are constantly working to improve the accuracy and quality of our AI-generated content. However, there may still be errors or inaccuracies. We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.





